Higher Education in Hungary
Education system
Hungarian higher education has been representing academic excellence for more than 650 years. The first university was founded in 1367 in Pécs, the Southern region of Hungary. Today, there are 64 accredited higher education institutions in Hungary and 4 foreign higher education institutions operating in Hungary with a license, ranging from minor universities of applied sciences to top research universities.
There are 6 statefunded, 37 privately-funded and 21 church-funded institutions to choose from. As a result of our institutions’ internationalisation process all students can find what fits their interests the best: institutions offer more than 700 courses in English, German, French and other languages. The foreign language programmes are of a high standard and tuition fees are very favourable when compared to its competitors.
The range of study fields students can choose from is wide:
- Agricultural science
- Arts Education, Arts, Arts and Humanities,
- Computer Science and Information Technology
- Economic Science
- Engineering Science
- Health Science
- Legal Science
- Natural Science
- Political Science and Public Governance
- Religion and Theology
- Social Science
- Sport Science
- Teacher Training
The largest institutions offer courses in all study fields while smaller institutions have programmes in a few specific areas. Students can earn double degrees at many universities through joint degree programmes in which the Hungarian university works together with another European higher education institution. In case of applying for these programmes students enrol in both universities and obtain a double degree from both institutions.
Higher education studies are offered at two types of higher education institutions, egyetem (university) and főiskola (college), both of them may offer courses in all three training cycles: Bachelor course, Master course and Doctoral course.
Although the degree structure is divided in most courses, there are some integrated (one-tier) programmes where the Bachelor level and the Master level is unified: veterinary medicine, architecture, dentistry, pharmaceutics, law and medicine. These one-tier programmes consist of 10-12 semesters (5-6 years) and by the end of the last year you must have 300 to 360 credits completed.
Within a Doctoral programme, you need to complete 240 credits within 4 years of study. At the end of the fourth semester, a comprehensive examination must be taken. After a successful examination, the last 2 years of the doctoral programme are about conducting the research and writing your dissertation, which can be extended with one more year.

Credit System
The European Credit Transfer System (ECTS) in Hungary ensures the transparency of the learning, teaching and assessment processes by facilitating recognition of your learning achievements and qualifications in many countries throughout the European Higher Education Area. The ECTS ensures that the grades you have achieved can be accepted by other European institutions in other countries.
At the end of each semester, the student’s study achievement is evaluated with a grade in the Hungarian five-grade scale. For incoming international students, a Transcript of Records must be issued that contains a table of completed courses, credits, the Hungarian grade and the ECTS grade.
The number of credits you have to achieve might differ from one institution and course to another in an academic year or semester, so you may need to approach your local international coordinator to obtain the relevant information about this.
The Hungarian academic credit system is an ECTS-compatible system. The calculation of the credits is based on the number of working hours of the students (one credit means 30 student working hours, on average).
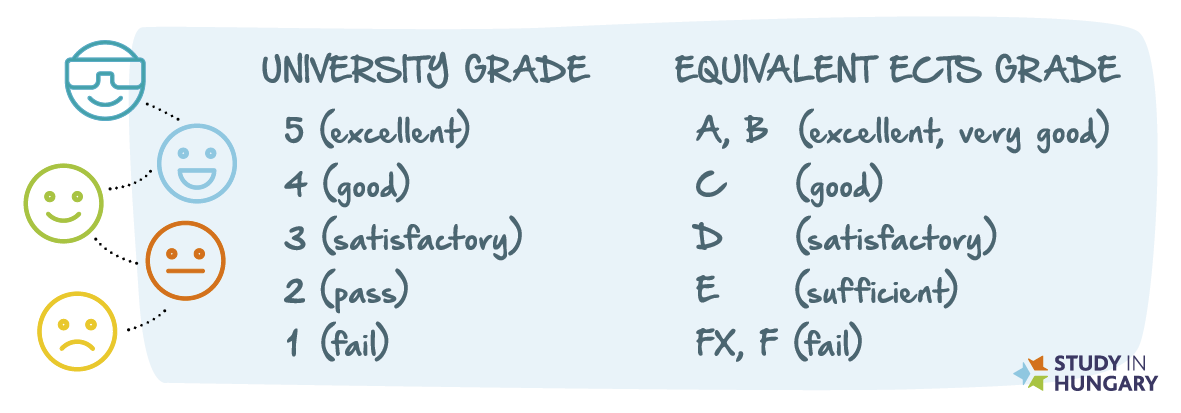
At the end of the semester, the student’s study achievement is evaluated with a grade (5-excellent, 4-good, 3-medium or satisfactory, 2-sufficient or pass, 1-fail). The ECTS conversion table ensures transfer procedures between the Hungarian academic credit system and the ECTS. The recognition of courses completed abroad is based on the credit transfer regulation.
For incoming international students, a Transcript of Records is issued at the end of the semester, which contains the code and title of the completed courses, credits, grade, and its ECTS-compatible grade.
ECTS grade compared with Hungarian grading:
Scholarships in Hungary
Erasmus+
If you are from the European Union, you are entitled to apply for Erasmus+ that provides opportunities for education, training, youth and sport.
You can also combine your study period in Hungary with a traineeship to gain work experience as Erasmus+ also offers internships. Opportunities to study in Hungary with Erasmus are available to students at Bachelor’s and Master’s levels, as well as Doctoral candidates. Students with physical, mental or health-related conditions may apply for additional funding after they have been selected to study. You can also gain some volunteer experience in Hungary through this programme for periods of 2 - 12 months or 2 - 8 weeks.
Programme countries:
- countries of the European Union
- + Iceland, Liechtenstein, Republic of North Macedonia, Norway, Serbia and Türkiye
Erasmus+ Traineeship
You can combine your studies with professional practice by taking an Erasmus internship in Hungary for a period of 3 to 12 months or you can only take part in an internship (2-12 months) without doing your studies at the same time. Your internship will be supported with a monthly stipend ranging from €500–€600 depending on the chosen country’s living standards; also it is possible to apply for an extra stipend of € 100 in specific cases.
Programme countries:
- countries of the European Union
- others: North Macedonia, Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, Serbia and Türkiye
Stipendium Hungaricum programme
The Stipendium Hungaricum Scholarship Programme was launched in 2013 by the Hungarian Government with the mission to increase the number of foreign students in Hungary and to encourage our education institutions to attract foreign students.
Study fields supported by the Stipendium Hungaricum Programme in 2023/2024
- Agricultural Science
- Arts Education, Arts, Arts and Humanities,
- Computer Science and Information Technology
- Economic Science
- Engineering Science
- Health Science
- Legal Science
- Natural Science
- Political Science and Public Governance
- Religion and Theology
- Social Science
- Sport Science
- Teacher Training
Full time studies:
- BA/BSc (undergraduate, 2-4 years)
- MA/MSc (graduate, 1,5-2 years)
- PhD studies (doctoral, 2+2 years)
- One-tier programme (5-6 years)
Part-time studies (one- or two-semester long exchange/part time studies – they can, but do not have to be, be part of the student’s degree studies in their sending higher education institutions)
Non degree programmes (professional and language preparatory courses, specialisation courses)
How does the SH programme contribute to your professional development?
- no tuition fee
- monthly stipend: for Bachelor or Master: cca. EUR 114, for Doctoral programmes: cca. EUR 365
- free dormitory places or contribution to private accommodation: EUR 104
- medical insurance
The expanding network of sending partners:
Arab Republic of Egypt, Argentine Republic, Belize, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Democratic Republic of São Tomé and Príncipe, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, Federal Republic of Nigeria, Federative Republic of Brazil, Georgia, Ibero-American General Secretariat (eligible member states: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba, Ecuador, El Salvador, Mexico, Peru, Uruguay, Venezuela), Islamic Republic of Iran, Islamic Republic of Pakistan, Japan, Kingdom of Cambodia, Kingdom of Morocco, Kingdom of Thailand, Kurdistan Regional Government/Iraq, Kyrgyz Republic, Lao People's Democratic Republic, Lebanese Republic, Malaysia, Mongolia, Montenegro, Oriental Republic of the Uruguay, Pacific Alliance (member states: Chile, Colombia, Mexico and Peru), State of Palestine, People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, People's Republic of Bangladesh, Republic of Burundi, People’s Republic of China, Republic of Albania, Republic of Angola, Republic of Azerbaijan, Republic of Belarus, Republic of Botswana, Republic of Cabo Verde, Republic of Chile, Republic of Colombia, Republic of Costa Rica, Republic of Cuba, Republic of Ecuador, Republic of Ghana, Republic of India, Republic of Indonesia, Republic of Iraq, Republic of Kazakhstan, Republic of Kenya, Republic of Korea, Republic of Kosovo, Republic of Liberia, Republic of Maldives, Republic of Mali, Republic of Moldova, Republic of Namibia, Republic of North Macedonia, Republic of Panama, Republic of Peru, Republic of Rwanda, Republic of Serbia, Republic of Seychelles, Republic of Sierra Leone, Republic of Singapore, Republic of South Africa, Republic of the Marshall Islands, Republic of the Philippines, Republic of the Union of Myanmar, Republic of Tajikistan, Republic of Turkey, Republic of Uganda, Republic of Uzbekistan, Republic of Yemen, Russian Federation, Saint Lucia, Socialist Republic of Vietnam, State of Eritrea, State of Israel, State of Kuwait, Sultanate of Oman, Syrian Arab Republic, Taiwan, The Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, Tunisian Republic, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, United Arab Emirates, United Mexican States, United Republic of Tanzania.
CEEPUS
If you are from Central Europe or the South-Eastern part of Europe, you are eligible to apply for the CEEPUS Programme (Central European Exchange Programme for University Studies) that aims to promote teacher and student mobility in Central and South-East Europe. Students can spend a study period abroad and teachers can undertake a teaching period at a partner university. These opportunities are designed to strengthen professional and personal relationships among Central European scholars. In Hungary the programme is managed by the Tempus Public Foundation.
Period of mobility:
- 1 semester (3-5 months)
- 1-2 months
- 3-5 days (short term excursion)
Member countries:
Albania, Austria, Bulgaria, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Czech Republic, Hungary, Macedonia, Moldova, Montenegro, Poland, Romania, Serbia, Slovenia, Slovakia and Kosovo
Funding
The funding of the programme is provided by the CEEPUS partner countries. Students receive their CEEPUS grant from the host country; therefore, the amount is tailored to local living standards.
Bilateral State Scholarships
Hungary has bilateral agreements with around 72 countries. Bilateral state scholarships are based on scientific and educational cooperation agreements signed by the governments of two countries. If your sending country has such an agreement with Hungary you may pursue a scholarship activity in Hungary as a nominee of your sending home country. It is also possible to apply individually, independently from your country, without being nominated.
"Scholarship types available (in 2023/2024):
- Student mobility: bachelor or master or doctoral semester/partial studies (3-5 months)
- Short Term Student mobility: for bachelor or master or doctoral students working on their diploma work (1-2 months)
- Short Term Excursion: for bachelor or master or doctoral students (3-5 days)
- Special Courses: like summer courses or intensive programmes (minimum 6 days)"
Scholarship Programme for Christian Young People
The core mission of the Scholarship Programme for Christian Young People is to provide the possibility of studying in Hungary to young Christian students who live in the crisis regions of the world and/or are threatened in their country because of their faith. After completing their studies, the scholarship holders will return to help their home community with their gained knowledge, and they will participate in the reconstruction of war-damaged countries and contribute to the improvement of the social situation and the preservation of the culture of Christian communities.
Scholarships are available for bachelor, master, one-tier master and doctoral programmes.
The Scholarship Programme for Christian Young People (SCYP) was founded in 2017 by the Government of Hungary.
The Scholarship Programme for Christian Young People is managed by the State Secretariat for the Aid of Persecuted Christians and for the Hungary Helps Program. The Hungary Helps Agency is in charge of coordinating the Scholarship Programme since August 2020.
Further information: https://hungaryhelps.gov.hu/about-the-programme/